The statistics released by IDC and Gartner this year show that the PC market has seen positive growth for the first time in six years. This is a big event for the PC industry. Because it can grow in the second quarter, the third quarter and the fourth quarter of the year are the peak season and further growth. It is not running. Unfortunately, the PC industry's manufacturers are too happy. During this time, Intel suddenly reported a shortage of 14nm capacity. The most exaggerated news is that the capacity gap is as high as 40%, and the shortage of supply will continue until the first half of next year.
The continuous extension of Intel's 10nm process is no longer news. How suddenly is the 14nm capacity insufficient? Since the end of 2015, Intel's 14nm has been in mass production for three years. Has it been so long before it says that the production capacity is insufficient? At first, this game did not have many players willing to believe, but the fact is that, and consumers have now felt the impact of 14nm capacity shortage. The eight-generation Core processor has increased in price, and the price of boxed and scattered films has risen almost every day. . Nine generations of Core has released three models, and the Core i9-9900K has not been listed until now.
These are the faults of Intel's 14nm capacity. This can be said to be the biggest thing in the PC industry in 2018, which has deeply affected consumers and even the entire PC industry, which will drag down the shipments of notebook manufacturers. The installed budget of DIY players will also be squeezed (select AMD).
Intel's global capacity distribution and 14nm fabs:
Unlike fabless semiconductor companies such as AMD and Qualcomm, Intel's operating model is IDM's vertical integration model, which is designed, produced, and tested by itself. Processors, semiconductor chip production is the core competitiveness of Intel processors, so Intel has been the most technologically advanced semiconductor company on the planet for 30 years.
As a global company, Intel has established large and small factories around the world in addition to semiconductor factories in the United States. The main distribution and process technologies are as follows:
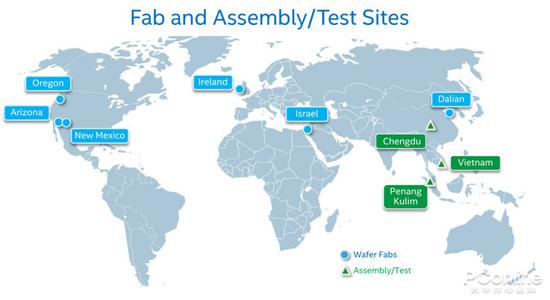
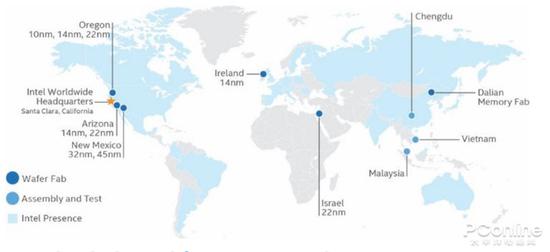
· Oregon, USA, with 22nm, 14nm and 10nm wafer fabs;
· Arizona, USA, 14nm and 22nm wafer fabs;
· New Mexico, USA, with two fabs of 32nm and 45nm;
· Ireland, with a 14nm process fab;
· Buffalo, Israel, with a 22nm process fab;
· There are two wafer fabs in Dalian and Chengdu in China, which were originally sealed and tested. However, the Fab 68 plant in Dalian has been converted into a 3D NAND fab before the end of September;
· There is a packaging factory in Vietnam and Malaysia.
In terms of production capacity, Intel now has three 14nm wafer fabs. This capacity is extremely high among global semiconductor companies. Anyway, in the first half of this year, there has been no shortage of production capacity in the first half of this year. It’s only a month, obviously something happened.
Intel official explanation of the lack of 14nm capacity, can you believe?
How did the 14nm process that has been produced for many years suddenly have a problem of insufficient capacity? There are a lot of rumors about this issue, but let's first take a look at what Intel officials say:
This year, continuous improvement in customer demand has driven the growth of Intel's business lines, bringing our revenue forecast for 2018 to $4.5 billion in January. Our supply will be able to meet our disclosed full-year revenue outlook, and we are working closely with our customers and factories to manage the various new requirements. -- Intel spokesman
According to Intel, the capacity crisis is due to high demand, resulting in Intel's revenue forecast for this year is expected to increase by 4.5 billion US dollars. Considering that Intel’s revenue last year was about 62.8 billion US dollars, and the increase of 4.5 billion US dollars is really quite a lot. It seems that the demand is really high, then what are the demand for those products?
Intel's processor mainly involves two parts, CCG client and DCG data center, which can be simply understood as consumption CPU and server CPU. Combine the financial data of Intel Q2 quarter to see the specific performance of these two parts of the business:
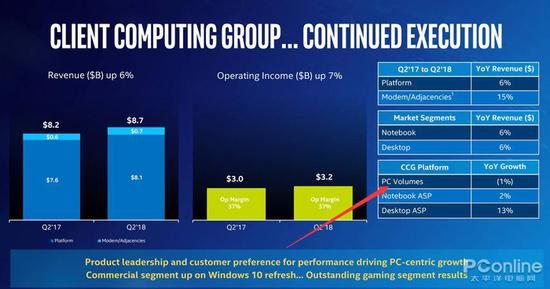
In the CCG department, Q2 quarter revenue was 8.7 billion US dollars, up 6% year-on-year, of which notebook market revenue increased by 6%, desktop market also increased by 6%, but revenue growth was mainly achieved by ASP average price, of which desktop processing The ASP price increased by 13%, and the notebook processor ASP increased by 2%. In terms of sales volume, shipments in the PC market in Q2 quarter actually fell by 1%.
PC market shipments fell by 1%. Obviously, the capacity is not enough. This pot is not caused by the PC market. PC players do not back this pot.
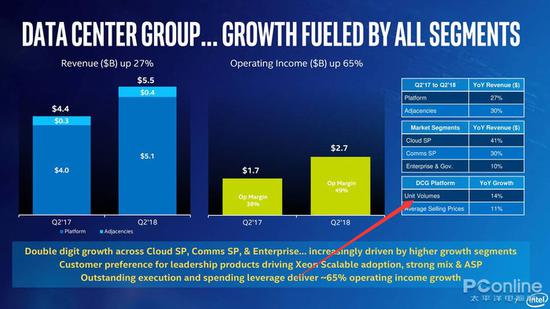
In the DCG data center department, Q2 quarter revenue was 5.5 billion US dollars, up 27% year-on-year. Cloud data and enterprise-level markets all experienced substantial growth, with the average price increasing by 11% and sales increasing by 14%.
In this case, Intel’s demand growth is still reasonable. The demand in the data center market is increasing sharply. However, this growth is unlikely to result in such a large out-of-stock shortage of 14nm capacity. There will be other reasons. It is most likely to count the following reasons.
One of the reasons for Intel's 14nm capacity shortage: the increase in multi-core chips leads to a decline in total output
Everyone knows that the processors are cut from a whole wafer. Intel is using 12-inch wafers. The total capacity is unchanged. Now the 14nm supply is insufficient, which means that each wafer produces less chips. And this is likely to be related to Intel's market changes in the past year. That is, under the pressure of AMD's multi-core processor, Intel has also followed the production of multi-core chips. The core increase means that the core area has also become larger. The total number of CPUs produced by the circle is less.
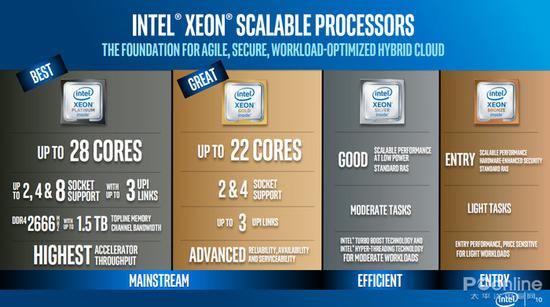
In 2017, AMD returned to the high-performance processor market with its Radon and EPYC processors. The mainstream AM4 desktop market is an 8-core 16-thread processor. The top TR4 platform is 16-core to 32-core, and the server-grade EPYC is 32-core. 64 thread processor. Although AMD's Acer processor is not as good as Core, but it can't hold more cores, so AMD processor has strong multi-core performance and high cost performance.
AMD's multi-core offensive has forced Intel to follow up. We can see that Intel launched the 18-core 36-thread Core i9 processor in 2017. The Core i7-8700K in the mainstream market has also been upgraded to 6-core 12-thread. The Core i5, i3 and Pentium are also upgraded to 6 cores, 4 cores, 2 cores and 4 threads, etc. This year, they continue to upgrade to 8 cores and 16 threads (i9-9900K) and 8 cores and 8 threads (i7-9700K).

In addition to the increase in processor cores in the consumer market, server processors are also increasing the number of cores. The Xeon series has increased from the previous 22 cores to 28 cores. This year's Cascade Lake series processors have not continued to increase the number of cores, but Intel is also AMD has begun to quietly cut prices, making the 20+ core Xeon processor more attractive and sales increasing.
Although Intel's advancement on multi-core processors has helped popularize 6-core and 8-core processors, the increase in core number means an increase in core area (with the same 14nm process), which means fixed wafer capacity. The number of CPUs produced will be less, and the more cores, the more difficult it is to produce, and the yield may be affected. 90% of the chips on the original 12-inch wafers are qualified, and now 6-8 cores are increasing. The yield may be reduced by 5% (the specific yield is unknown, the number is just an analogy), which also leads to a decrease in the number of CPUs.
The second reason for Intel's 14nm capacity shortage: 300 series chipset upgrade 14nm process
In addition to the reduction in capacity output caused by the increase in multi-core processors, Intel has another move that led to the 14nm capacity crisis. That is, Intel decided to switch the 300 series chipset to the 14nm process. This adjustment will cause the chipset to compete with the processor. Increased the outbreak of the production crisis.
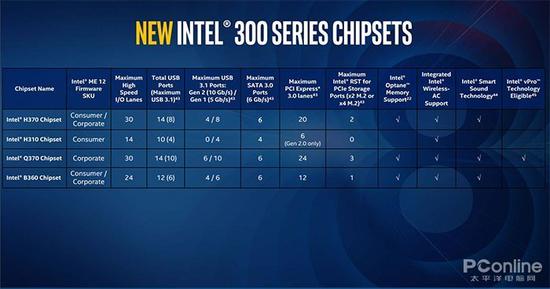
Intel's 300-series chipset codenamed Cannonlake PCH, including the just released Z390, H370, Q370, B360 and H310, and now the flagship chipset Z370 is not in the true 300 series chipset, because it is actually 22nm process Z270 Vest.
The use of 14nm process to produce chipsets can help improve chipset power consumption, but the benefits are not obvious, because the 22nm process Z370 chipset TDP power consumption is also 6W, the chipset's function is relatively simple, completely less advanced The process, but the chipset and the CPU are one-to-one, and global PC shipments exceed 3 per year. More than 100 million, Intel's share is more than 80%, even if the latest platform only accounts for 1/4 of the number, the 14nm chipset required is also massive, and the 14nm capacity is a serious test.

Because of this, after the 14nm capacity issue, Intel was exposed to adjust the chipset's 14nm production plan, the entry-level H310 chipset was changed back to 22nm process production, and the improved H310C chipset was exposed on the Internet. H310 is slightly higher.
In addition to the H310 chipset, there is also a rumor that the B360 chipset has cut production by 30% recently. This is part of Intel's 14nm capacity improvement, but it may lead to the shortage of B360 motherboards in Q4.
Intel's 14nm capacity shortage is the third reason: to ensure the big customer Apple baseband
If the first two factors are the internal factors of Intel's 14nm capacity shortage, then this is an external factor, and it may become the most critical factor, that is, the baseband orders for Apple iPhone XS/XS Max/XR mobile phones are all provided by Intel this year. It is the XMM7560 baseband of the 14nm process.
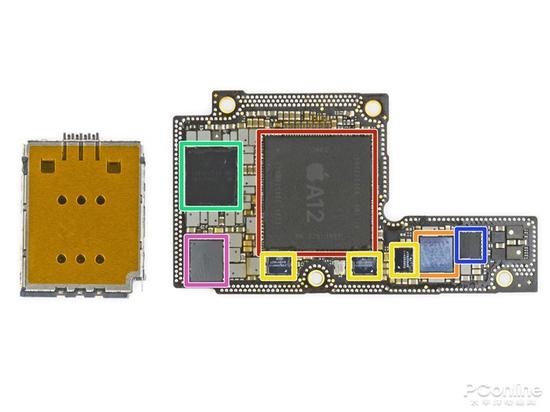
Intel smashed its head in the past few years and wanted to enter the mobile market. In the end, it fell back and sold more than 7 billion US dollars, but this year Intel won the treasure - because Apple and Qualcomm's patent war has not yet ended, in order to put pressure on Qualcomm This year's iPhone baseband processor orders have all been given to Intel, Qualcomm has been out, so Apple's supply chain for the baseband chip is very demanding, and Intel is also happy to win such a large order, naturally to protect Apple's supply.
Even if you don't consider some of the baseband on the iPhone 8/8 Plsu/X, just this year's iPhone XS/XS Max/XR baseband is enough for 14nm. According to Guo Mingwei, an analyst at Tianfeng Securities, Apple’s next-generation iPhone will reach 80-90 million units this year, which will require at least 80 million baseband chips, and the stocking volume will be higher than the shipment. Visible light is a baseband chip that can account for a large portion of Intel's 14nm capacity. Most of the $4.5 billion in revenue this year will be contributed by baseband chips.
The consequences of the Intel 14nm capacity crisis: the overall price increase of bulk boxed processors
For consumers, the reason why Intel's 14nm capacity is insufficient is not important, because now we have already assumed the consequences of this crisis. In the past two months, the eight-generation Core processor has been in full or even out of stock in both boxed and bulk, especially the processor with superior cost performance, such as Core i5-8400, Core i3-8100, and Pentium G4560. Netizens can only ridicule the eight-generation processor this year and become a wealth management product.
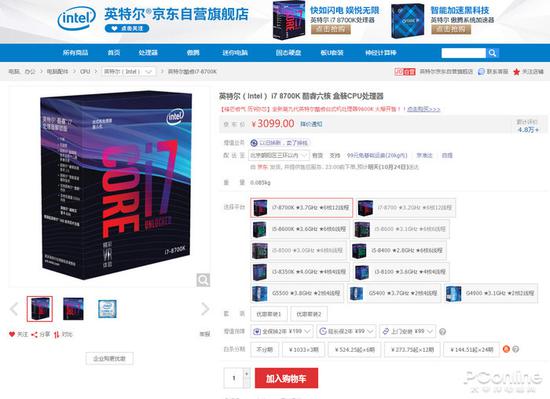
The current boxed price of the Core i7-8700K has risen to 3099 yuan, the previous price is only 2799 yuan, and the lowest price can be 2,000 yuan, and now it has risen a lot.
The price of the Core i5-8400 is less than 1,000 yuan. Today, the price is generally 1400 yuan, and the box is more than 1999 yuan. This kind of increase has already made people unable to get down.
Not only the price of the eight-generation Core processor, but also the price of the nine-generation Core processor just released is obviously affected by the capacity. The 8-core 16-thread Core i9-9900K is priced at 4,999 yuan. This price has broken through the mainstream Core processing. The limit of the device, and has not been sold until now, the price is expensive, the supply is still small, and the players who are interested in purchasing the nine-generation Core processor are also more helpless.
AMD, Intel is going to kill him? The ideal is very beautiful
This year's PC market has finally ushered in the first growth in six years, but the Intel 14nm capacity crisis has disrupted this rhythm. PC players who suffer from processor price increases and out-of-stocks are not worried. Some people may think that Intel's capacity is insufficient to buy AMD. Some people are optimistic about AMD's full-year share growth. The most exaggerated statement is that AMD's market share this year can be Reaching 30% is three times the current level.
This goal is very good and powerful. Taking advantage of Intel's capacity crisis, AMD's theoretical listing has the opportunity to expand its market share. But how many markets can be taken from Intel is the problem. The first solution is AMD's own production capacity. problem.
We all know that the Ruilong processor is produced by the foundry Globalfoundries' 14nm LPP process. The Ruilong II released in April this year is produced by the improved 12nm LPP process. The production base is Globalfoundries (hereinafter referred to as GF) in the US. Fab 8 fab in Malta, New York, and the only fab.
Compared with Intel's three 14nm fabs, GF's 14/12nm fab has only one, and the production time is only one year. Considering the glory history of GF's previous problems in yield, Fab 8 is now The production capacity has reached the limit, and GF's financial situation in recent years is still not optimistic. There is no money to invest in increasing production capacity. Therefore, even if AMD has the opportunity to seize the share from Intel, the reality is very helpless. GF can't quickly increase the processing of Ruilong. Capacity of the device.
Market research firm Mercury Research recently announced AMD's desktop CPU market share change from 2016 to 2018 Q2. AMD's share in Q3 2016 was only 9.1%. It was only after the launch of the Athlon processor in Q1 2017. Growth, not the end of the year, is 12%, reaching 12.2% in Q1 this year and 12.3% in Q2.
At this rate, AMD's optimistic desktop market share this year is estimated to be at most 15%. The rumored 30% share is basically impossible unless the Q4 shipments can increase by 250%, or Intel shipments. Plunging 65%, but from the best record in history since 2000, Intel has fallen by up to 24% of shipments, and AMD's best growth is only 57%.
You know, this is still the share of the desktop CPU market. In the notebook and server market, AMD's share is lower, and it will not change much this year.
In addition to the rapid increase in production capacity, AMD is also facing the problem of the competitiveness of the processor itself. The second-generation Ruilong's Ruilong 7 2700X has narrowed the gap with Intel's eight-generation Core processor through frequency boost and power optimization, but This year, Intel introduced a nine-generation Core processor, adding an 8-core 16-thread processor, while the single-core frequency has been increased to 5GHz. The other two processors have also increased the number of cores and single-core frequencies, and the performance has been opened again with AMD. gap.
AMD wants to reverse the gap in processor performance, can only wait for the Zen 2 architecture and 7nm process, the current 7nm CPU has been sampled, the first EPYC server product, consumer level to be followed, the release time has not been announced, but there is news that it is In the second half of 2019, by virtue of the advantages of technology and architecture, it is possible for AMD to close the gap with Intel Core processors.


